When planning research in China it’s essential to appreciate, and take into account, the tier systems and how they impact audience targeting.
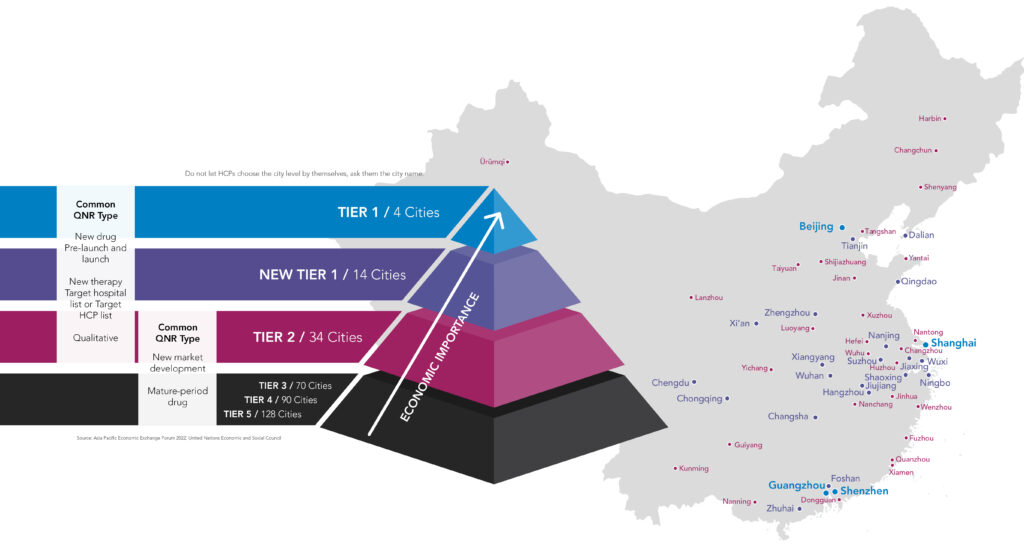
Cities in China are classified by a tier system, which incorporates economic development, population, ease of living, happiness etc to allocate each city to one of five tiers. Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen are the four major metropolitan areas, but we are expecting to see 14 new cities be assigned tier one status in 2022.
When you’re planning your research and target markets, your choice of tier is important, and you should consider adjusting target cities based on their tier and your research topics and objectives. In large hospitals in higher-tier cities, doctors will have more experience treating incurable diseases, and rare diseases. Another consideration is that new treatment methods and drugs are normally introduced in higher tier cities first.
Medical and Health
Institutions There are over one million medical and health institutions in China including hospitals, community medical institutions, and professional public health institutions, split into three tiers, with tier three the highest. Each tier then also has grades A, B, and C. Hospitals in tiers two and three benefit from better access to resources, and are often pioneers of new policies, drugs, with practitioners using advanced medical technology. By contrast, tier one hospitals provide broader basic medical services. ‘Community medical institutions’ includes community healthcare centres, clinics, and township / rural clinics. The professional public health institutions include disease control and prevention centres, specialist disease prevention institutes, and healthcare supervision centres.
Community medical institutions treat chronic disease patients in time by providing long-term care and are staffed by general practitioners who are also responsible for ensuring that medical resources are used as efficiently as possible.


